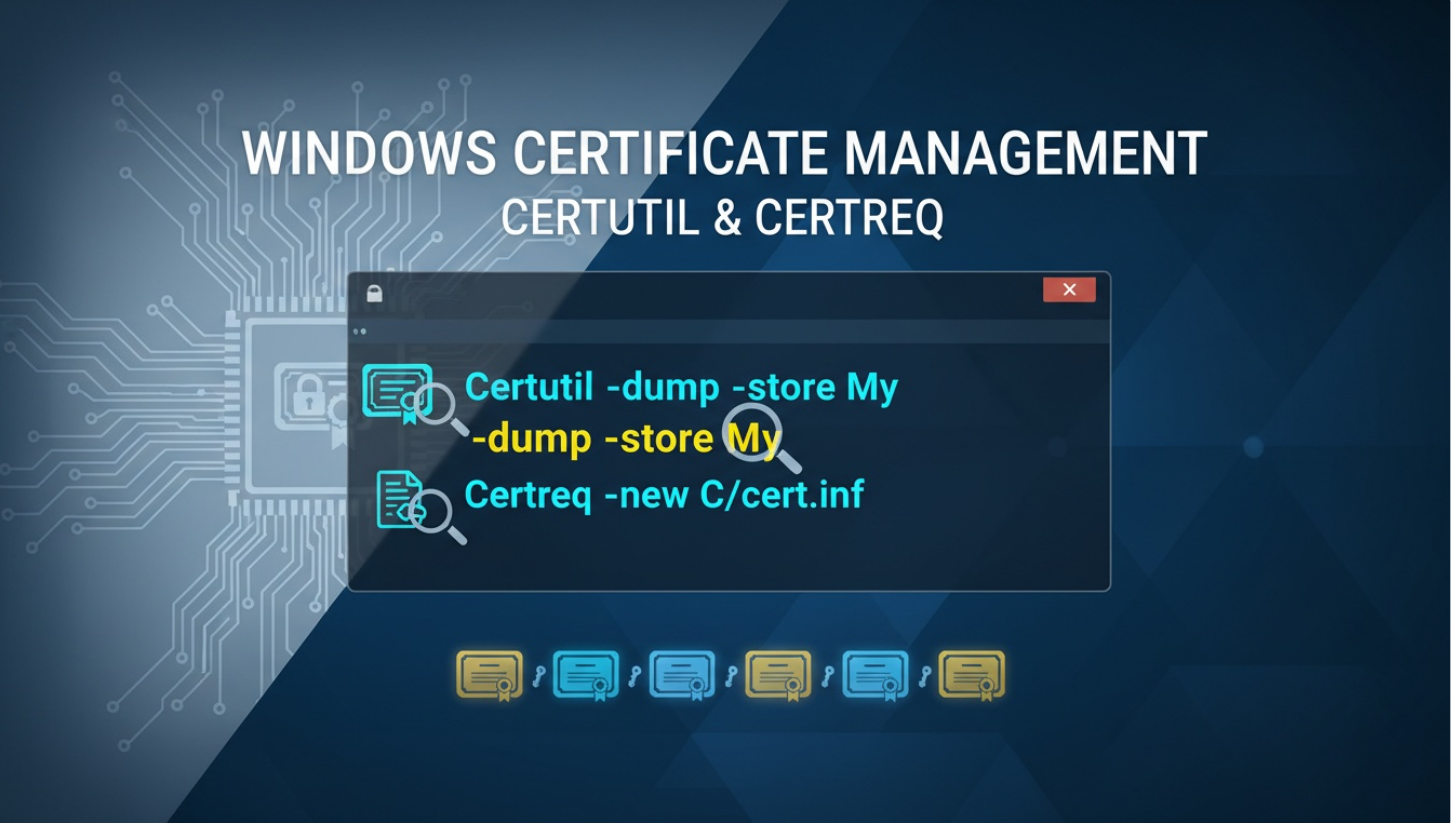
Discover the most powerful certutil commands, including certutil -pulse, certutil -hashfile, certutil -dspublish, and more
Introduction
If you have ever managed certificates on Windows, you have almost certainly touched Certutil and Certreq. These tools are usually introduced as simple utilities for requesting, installing, or inspecting certificates. In reality, they are far more powerful than their surface-level documentation suggests.
Hidden behind sparse help text and decades of backward compatibility are switches that expose deep visibility into certificate stores, Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS), and the full lifecycle of X.509 certificates. Many of these switches are rarely discussed, yet they are used daily by experienced PKI engineers to troubleshoot complex enterprise issues.
This guide pulls back the curtain. We explore the lesser-known and undocumented switches of Certutil and Certreq, explain how they work, and show where they fit into modern enterprise, cloud, and Zero Trust environments.
What This Guide Covers
- Why Certutil and Certreq still matter in modern PKI
- Hidden and advanced switches administrators rarely document
- How these switches expose certificate internals
- Real enterprise troubleshooting scenarios
- Secure usage patterns and operational risks
- How these tools compare to modern PKI platforms
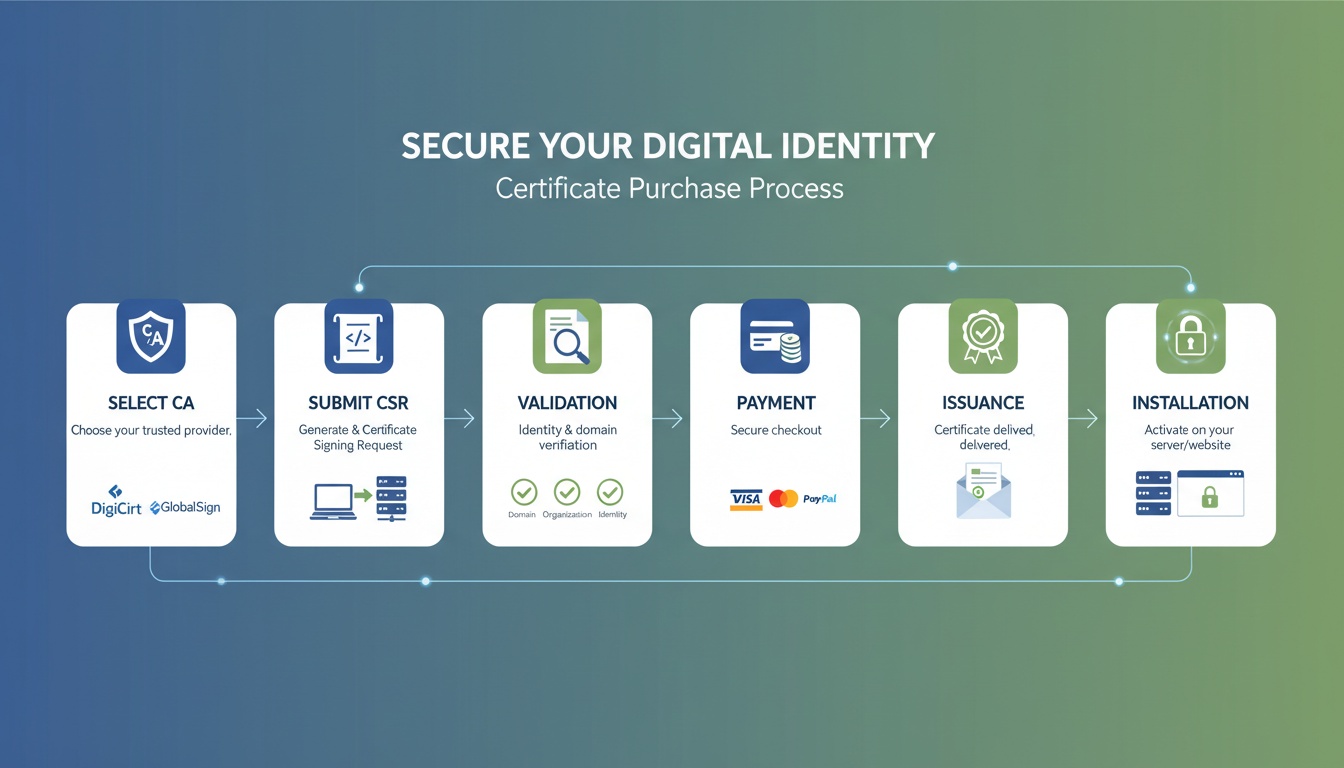
Workflow Diagram Overview
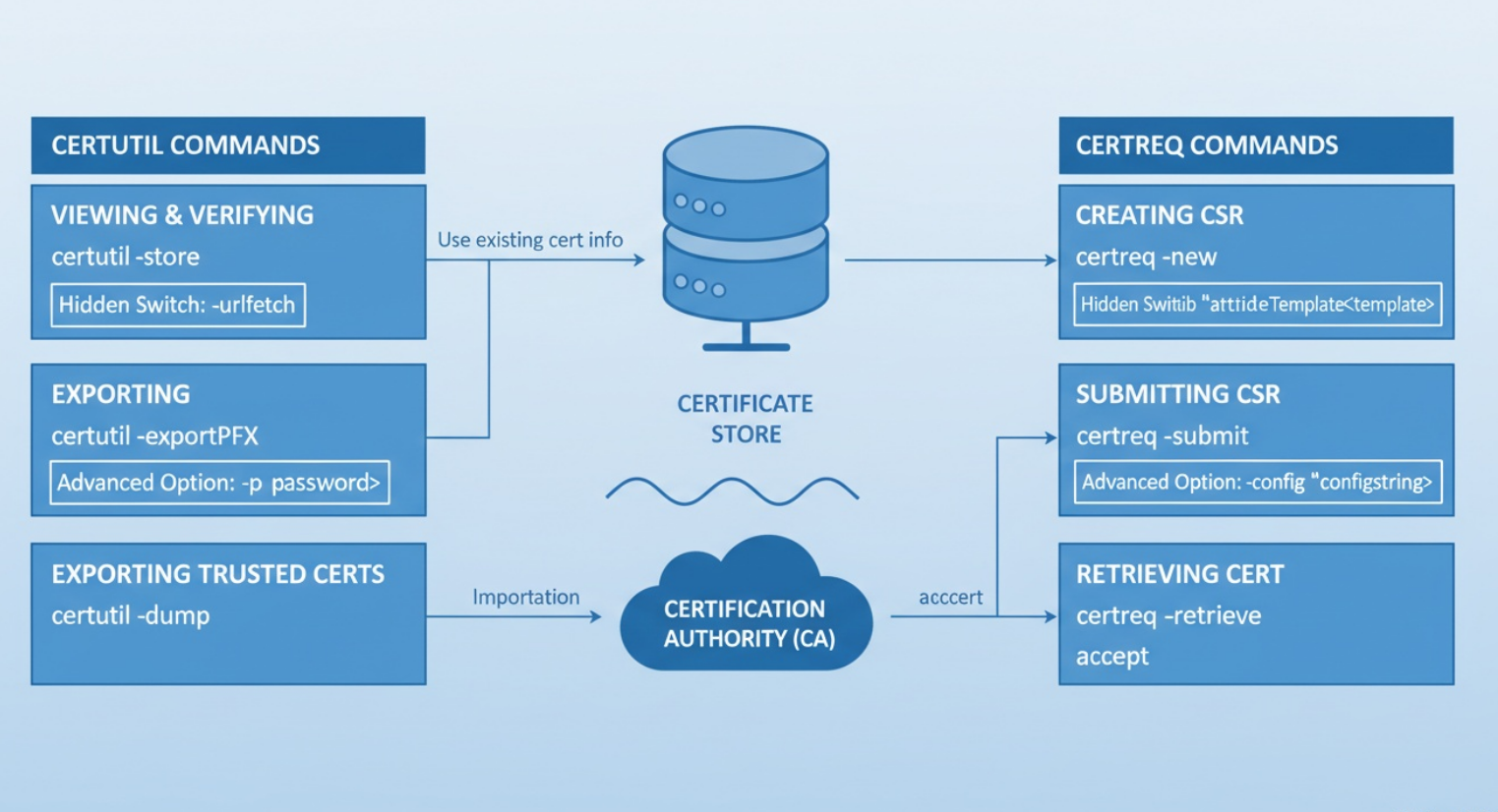
- Certreq focuses on certificate enrollment
- Certutil focuses on certificate inspection and validation
- Together they span the full certificate lifecycle
- Hidden switches reveal what GUI tools abstract away
1. What Are Certutil and Certreq?
Certreq
- Native Windows tool for certificate enrollment
- Generates certificate signing requests (CSRs)
- Submits requests to Certificate Authorities
- Accepts and installs issued certificates
- Interacts with enrollment policies and templates
Certutil
- Diagnostic and management tool for PKI
- Inspects certificate stores
- Queries CA databases
- Verifies certificate chains and revocation
- Dumps raw ASN.1 structures
2. Why Certutil and Certreq Matter Today
- Windows PKI still underpins most enterprise trust
- Used for:
- TLS and mTLS
- Kerberos and LDAPS
- Device and machine identity
- Smart cards and VPN authentication
- Hybrid cloud environments rely on on-prem PKI anchors
- Zero Trust strategies depend on certificate-based identity
- Native tools provide visibility automation platforms often hide
3. How Certutil and Certreq Work
Component 1: Certificate Store Management
- certutil.exe reads and repairs stores
- certutil -repairstore reassociates orphaned private keys
- Helps after OS rebuilds, migrations, or profile corruption
Component 2: Auto-Enrollment Refresh
- AD CS clients normally wait for policy refresh
- certutil -pulse forces immediate retrieval of templates and new certificates
- Critical in enterprise environments
Component 3: Active Directory Publishing
- CAs must publish CRLs, AIAs, and NTAuth certificates
- certutil -dspublish ensures objects are visible to domain members
Component 4: Cryptographic Hashing
- certutil -hashfile verifies certificate bundles, CRLs, scripts, executables
Component 5: CA Registry Configuration
- certutil -setreg changes CA lifespan, CRL intervals, audit settings
- Used to tune issuance behavior
4. Architectural Workflow of Certutil and Certreq
Certificate Enrollment and Validation Flow
Client System
|
| certreq -new
| Creates CSR from INF
v
Certificate Request File
|
| certreq -submit
| Submits request to CA
v
Issuing Certificate Authority
|
| Policy Module
| Template Validation
| Key Usage Checks
v
Issued Certificate
|
| certreq -accept
| Installs certificate
v
Local Certificate Store
|
| certutil -store
| certutil -dump
| certutil -verify
v
Chain Building and Validation
|
| AIA Retrieval
| CRL / OCSP Checks
v
Trust DecisionHidden switches expose each of these internal steps, making it possible to debug failures that would otherwise be opaque.
5. Real Code Snippets
Example 1 - Trigger Auto-Enrollment
# Forces Windows to immediately refresh certificate templates
certutil -pulseExample 2 - Repair a Certificate Store
# Attempts to reassociate orphaned certificate keys
certutil -repairstore my <SerialNumber>Example 3 - Publish CRL/AIA Objects to Active Directory
# Publishes CRL or AIA locations
certutil -dspublish <file.crl> CRLExample 4 - Compute Hash of a Certificate or File
# SHA256 hash of a file
certutil -hashfile mycert.cer SHA256Example 5 - Modify Windows CA Registry Settings
# Updates CA configuration parameters
certutil -setreg CA\CRLPeriodUnits 1Example 6 - Submit a CSR using certreq
certreq -submit -config "CA01\Domain-CA" request.req request.cer6. Hidden and Advanced Certutil Switches
- certutil -store -v
- Displays verbose certificate metadata
- Reveals extensions hidden from GUI tools
- certutil -verify -urlfetch
- Forces CRL and AIA retrieval
- Exposes network and firewall issues
- certutil -dump
- Outputs raw ASN.1 structures
- Used for malformed or non-compliant certificates
- certutil -dcinfo
- Validates domain controller certificates
- Critical for Kerberos and LDAPS troubleshooting
7. Hidden and Advanced Certreq Switches
- certreq -new -q
- Suppresses prompts
- Enables automation
- certreq -submit -attrib
- Explicitly selects certificate templates
- Avoids policy ambiguity
- certreq -accept
- Installs certificates silently
- Associates certificates with private keys
- certreq -policy
- Displays enrollment policies
- Explains why requests fail before CA submission
8. Best Practices
- Use advanced switches only when necessary
- Test all commands in non-production environments
- Restrict Certutil access on CA servers
- Log command execution for auditing
- Avoid exposing private key material
- Combine with PowerShell for controlled automation
- Validate certificate chains after enrollment
- Monitor CRL and AIA availability
- Apply least privilege to PKI administrators
- Document internal PKI runbooks
- Regularly audit CA configuration
- Integrate outputs with SIEM tools
- Rotate credentials used in automation
- Enforce template governance
- Treat Certutil as a privileged diagnostic tool
9. Common Pitfalls
- Running Certutil with excessive privileges
- Misinterpreting verbose ASN.1 output
- Assuming GUI tools show all certificate details
- Ignoring network dependencies during validation
- Hardcoding template names in scripts
- Skipping revocation checks
- Mixing user and machine certificate stores
- Overusing dump outputs in shared environments
- Failing to validate post-installation trust
10. Advanced Enterprise Use Cases
- CI/CD pipelines issuing short-lived certificates
- Zero Trust device and workload identity audits
- Hybrid cloud trust validation
- Multi-forest PKI troubleshooting
- IoT and edge device provisioning
- mTLS enforcement in internal services
- Incident response and forensic analysis
Keyword Expansion Zone
- certutil hidden switches
- certreq advanced usage
- Windows PKI troubleshooting
- AD CS diagnostics
- certificate chain validation Windows
- enterprise PKI automation
- Zero Trust certificate identity
Competitor Comparison
How QCecuring stacks up against major competitors in enterprise PKI automation and certificate lifecycle management:
| Feature | QCecuring | DigiCert | Venafi | Keyfactor | Encryption Consulting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Key Rotation | Advanced | Basic | Good | Comprehensive | Manual |
| HSM Integration | Native | Partial | Full | Enterprise | Limited |
| Cloud Platform Support | All Major | Select | Broad | Extensive | Few |
| Zero Trust Alignment | Built-in | Add-on | Integrated | Framework | Custom |
| API-First Architecture | Yes | Limited | Yes | Yes | Legacy |
| Real-time Monitoring | Continuous | Scheduled | Near-real | Live | Batch |
- QCecuring
- Designed for enterprises that require deep PKI visibility and strong automation
- Emphasizes native Zero Trust alignment rather than bolt-on features
- API-first design supports CI/CD, cloud-native workloads, and hybrid environments
- Continuous monitoring enables faster detection of certificate and key risks
External Resources
Final Summary
- Certutil and Certreq go far beyond basic usage
- Hidden switches expose critical PKI internals
- These tools remain essential in hybrid enterprises
- Advanced usage requires discipline and controls
- Modern platforms complement native tooling
FAQs
Q: Are hidden Certutil switches supported? Many are supported but under-documented; testing is essential.
Q: Can Certreq be automated safely? Yes, with least privilege and controlled templates.
Q: Is Certutil dangerous?? Only when misused; access should be restricted.
Q: Do these tools work in the cloud? Best suited for hybrid PKI models.
Q: Why not use only PKI platforms? Native tools provide diagnostic depth platforms abstract.
Q: Are Certutil and Certreq deprecated? No, they remain core Windows PKI components.
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.