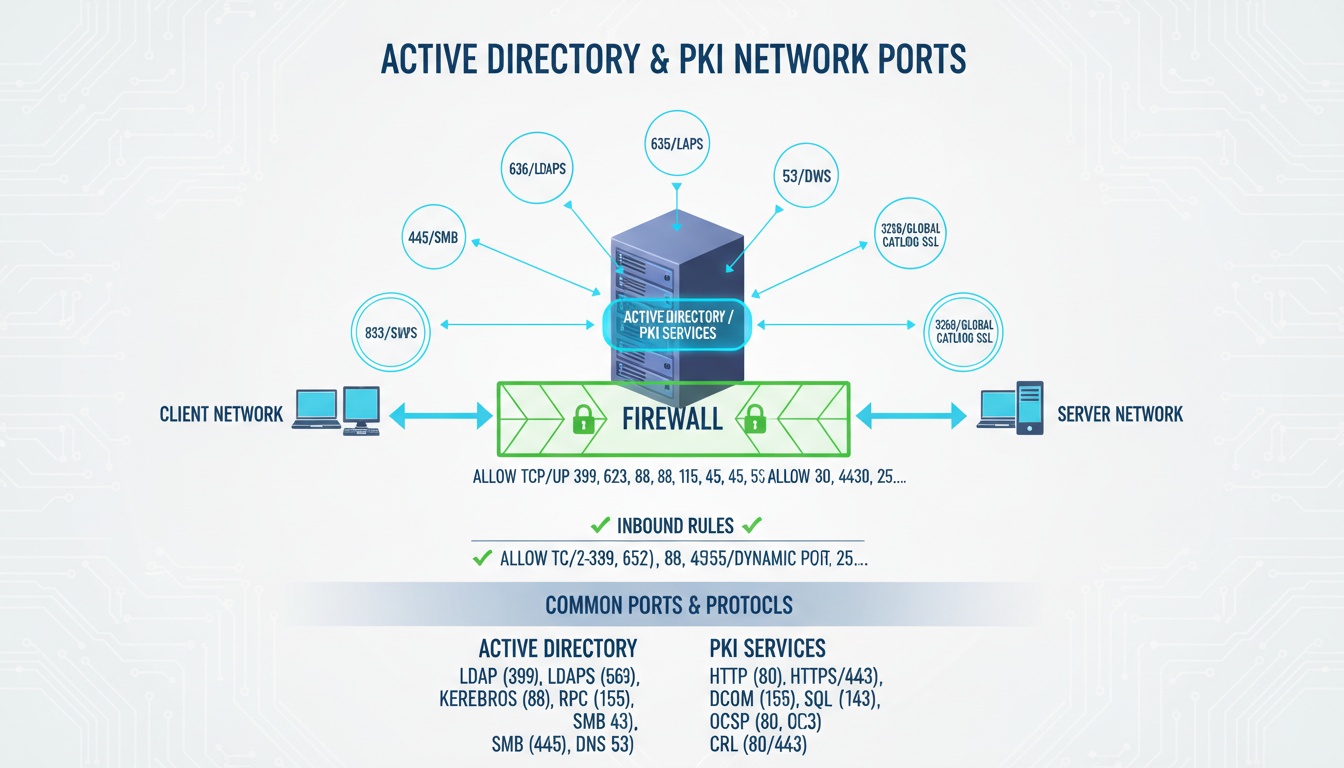
Essential network ports and protocols for AD and PKI infrastructure
Every enterprise network depends on Active Directory and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for authentication, authorization, and secure communications.
However, these services require specific network ports to function properly and misconfigurations can bring your infrastructure to a halt.
Whether you’re deploying domain controllers, setting up certificate authorities, or configuring firewalls, understanding these port requirements is critical for:
- Seamless domain authentication
- Secure certificate issuance
- Proper replication between servers
- Successful network segmentation
This guide breaks down all the essential ports in a clear, technical way.
What This Guide Covers
- Core Active Directory ports
- Dynamic port ranges
- PKI Certificate Authority requirements
- Certificate distribution points
- Firewall best practices
- Troubleshooting techniques
- Real-world deployment examples
1. What Are Active Directory and PKI Ports? (Simple Definition)
Active Directory and PKI ports are specific network endpoints that enable communication between domain controllers, certificate authorities, clients, and other infrastructure components.
These ports ensure:
- Secure authentication via Kerberos and LDAP
- Proper certificate enrollment and validation
- Reliable replication between servers
- Encrypted communications
Without the right ports open, your network services won’t work.
2. The Core Components That Require Network Access
A complete AD/PKI infrastructure contains these service types:
Domain Controllers
- Handle authentication and directory services
- Store user and computer accounts
- Manage group policies
- Replicate directory data
Certificate Authorities
- Issue and sign digital certificates
- Maintain certificate revocation lists
- Handle certificate enrollment requests
- Validate certificate chains
Client Workstations
- Authenticate to domain controllers
- Request and renew certificates
- Validate certificate chains
- Access network resources
3. Visual Diagram: AD and PKI Port Architecture
Client Workstations ←→ Domain Controllers ←→ Certificate Authorities
↑ ↑ ↑
Various Ports Core AD Ports PKI PortsThis architecture shows how different components communicate through specific ports.
4. Why Specific Ports Matter for Security
Proper port configuration provides:
- Network segmentation control
- Attack surface reduction
- Compliance adherence
- Auditing capabilities
- Secure service isolation
Incorrect port configurations can lead to security vulnerabilities and service outages.
5. Core Active Directory Ports (Always Required)
When setting up domain controllers, these ports are essential:
-
DNS - Port 53 (UDP/TCP)
- Domain Name System resolution
- Critical for domain member discovery
-
Kerberos - Port 88 (UDP/TCP)
- Authentication protocol
- Ticket granting and validation
-
RPC Endpoint Mapper - Port 135 (TCP)
- Remote Procedure Call coordination
- Service binding point
-
NetBIOS - Ports 137-139 (UDP/TCP)
- Legacy name resolution and session services
- Still required for older systems
-
LDAP - Port 389 (UDP/TCP)
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- Directory queries and updates
-
SMB/CIFS - Port 445 (TCP)
- File sharing and domain join
- Group Policy application
-
Kerberos Password Change - Port 464 (UDP/TCP)
- Password updates
- Account management
-
LDAPS - Port 636 (TCP)
- Secure LDAP
- Encrypted directory queries
-
Global Catalog - Ports 3268-3269 (TCP)
- Universal group membership queries
- Multi-domain authentication
6. Dynamic Port Range Requirements
Active Directory also uses dynamic RPC ports:
- Windows Server 2008 and later: 49152-65535
- Older systems: 1024-5000
These dynamic ports support:
- Directory Replication (DFSR)
- File Replication Service (FRS)
- Exchange Server communications
- Certificate Services
7. PKI Certificate Authority Ports
Certificate Authorities require these ports:
-
HTTP - Port 80 (TCP)
- Certificate enrollment (redirects to HTTPS)
- CRL distribution
-
HTTPS - Port 443 (TCP)
- Secure certificate enrollment
- Certificate management portals
-
RPC Endpoint Mapper - Port 135 (TCP)
- CA administration
- Certificate templates management
-
Dynamic RPC - 49152-65535 (TCP)
- CA operations
- Certificate issuance processes
8. Certificate Distribution Point Ports
For certificate validation, these ports are needed:
- HTTP - Port 80 (TCP): CRL distribution
- HTTPS - Port 443 (TCP): Secure CRL distribution
- LDAP - Port 389 (TCP): Certificate publication in AD
9. Common Configuration Errors
Typical mistakes include:
- BLOCKED_PORT_ERROR
- RPC_UNAVAILABLE
- KERBEROS_AUTH_FAILED
- CERT_ENROLL_DENIED
Root causes:
- Firewalls blocking essential ports
- Incorrect dynamic port range configuration
- Missing service dependencies
- Network segmentation issues
10. What Network Administrators Should Do
Network teams should:
- Map all required ports before deployment
- Configure firewalls with explicit rules
- Monitor port usage and anomalies
- Document port requirements for audits
- Test connectivity before production
11. Enterprise Deployment Considerations
In enterprise environments, consider:
Network Segmentation
- Isolate critical infrastructure
- Use jump servers for administration
- Implement zero-trust principles
High Availability
- Load balance domain controllers
- Cluster certificate authorities
- Replicate across sites
Monitoring
- Watch for port scanning attempts
- Alert on unauthorized access
- Log all authentication events
12. Best Practices for Port Management
- Document all required ports
- Use minimal port exposure principle
- Automate firewall rule deployment
- Regularly audit open ports
- Implement intrusion detection
- Follow Microsoft security guidelines
- Use IPsec for encryption
- Monitor certificate expiration
13. Keyword Integration Zone
active directory ports • pki ports • certificate authority ports • domain controller ports • network security ports • firewall configuration • port 389 • port 443 • port 445 • port 135
(Each appears once only.)
14. External References
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/networking/service-overview-and-network-port-requirements
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/windows-firewall/best-practices-configuring
- https://www.cabforum.org/
****
Need help managing AD/PKI ports, internal PKI, automation, Zero Trust identity, or enterprise TLS workflows?
Qcecuring delivers secure, automated PKI and certificate lifecycle platforms.
Final Summary (5 Key Points)
- Active Directory requires ports 53, 88, 135, 389, 445, 464, 636, and 3268-3269
- PKI services need ports 80, 443, 135, and dynamic RPC ranges
- Dynamic ports 49152-65535 are essential for AD operations
- Certificate distribution requires ports 80, 443, and 389
- Proper firewall configuration prevents outages and security issues
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.