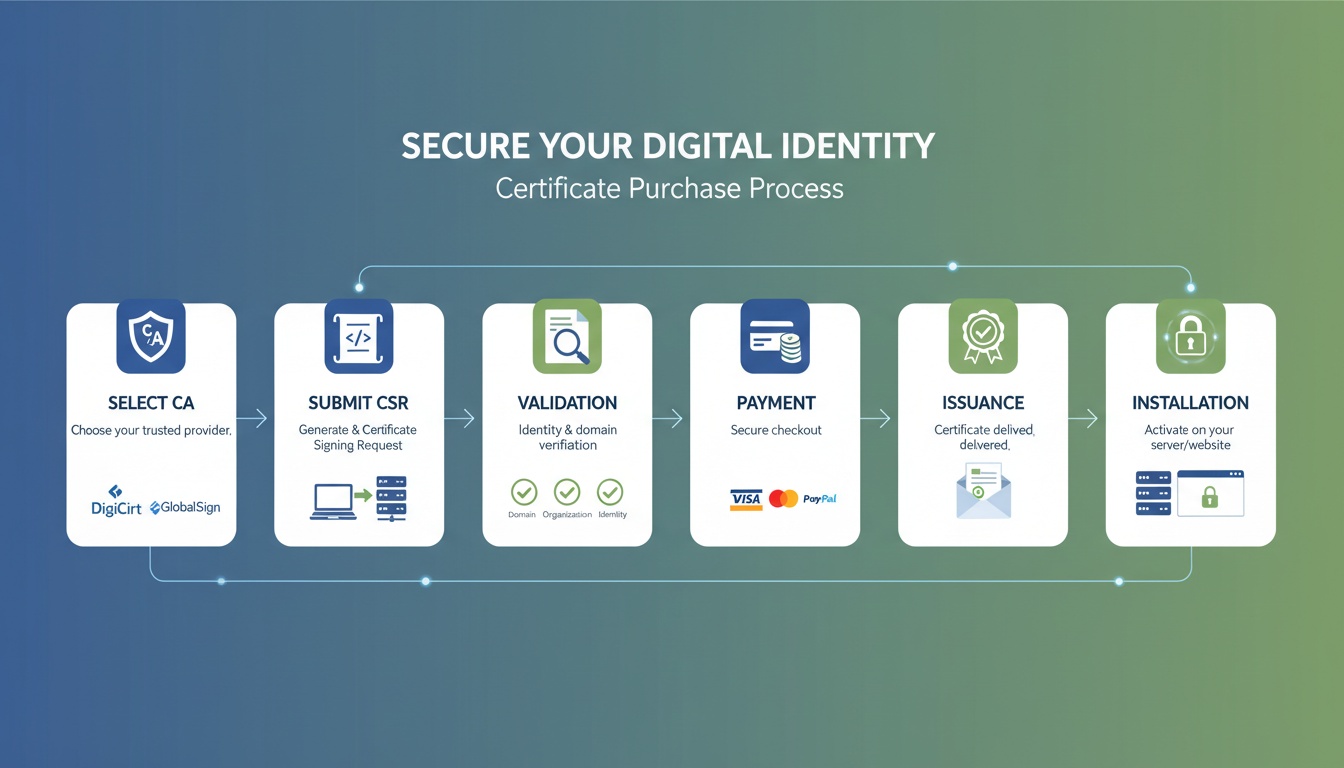
Why SFTP is the preferred method for secure file transfers in modern enterprises
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) and Its Advantages: A Complete Guide
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, transferring files securely between systems is more critical than ever.
Enter Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) – the go-to solution for organizations that prioritize data security and regulatory compliance.
Whether you’re moving financial records, customer data, or application binaries, SFTP provides:
- End-to-end encryption
- Strong authentication mechanisms
- Comprehensive audit trails
- Industry-standard security controls
This guide explains everything you need to know about SFTP and why it’s superior to legacy file transfer methods.
What This Guide Covers
- SFTP definition and how it works
- Key advantages over FTP and FTPS
- Encryption and authentication mechanisms
- Enterprise use cases
- Implementation best practices
- Security considerations
- Comparison with alternative protocols
1. What Is Secure File Transfer Protocol? (Simple Definition)
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a network protocol that provides secure file access, transfer, and management over any reliable data stream.
It’s important to note that:
- SFTP is not the same as FTPS
- It runs over SSH (Secure Shell)
- It encrypts both commands and data
- It’s widely supported across platforms
SFTP essentially extends SSH capabilities to include file transfer functionalities.
2. The Core Components of SFTP Architecture
An SFTP implementation involves these key components:
SSH Server
- Listens for SFTP connections
- Authenticates clients
- Manages file system access
- Enforces security policies
SSH Client
- Initiates SFTP sessions
- Handles authentication
- Provides user interface
- Manages local file operations
Encryption Layer
- Secures data in transit
- Protects credentials
- Ensures integrity
- Prevents eavesdropping
3. Visual Diagram: SFTP Connection Flow
graph TB
A[SSH Client] -->|1. Authentication| B(SSH Server)
B -->|2. Channel Setup| C[SFTP Subsystem]
C -->|3. Encrypted Transfer| D[(File System)]
style A fill:#e1f5fe
style B fill:#e8f5e8
style C fill:#fff3e0
style D fill:#fce4ecThis flow shows how SFTP establishes secure connections through SSH.
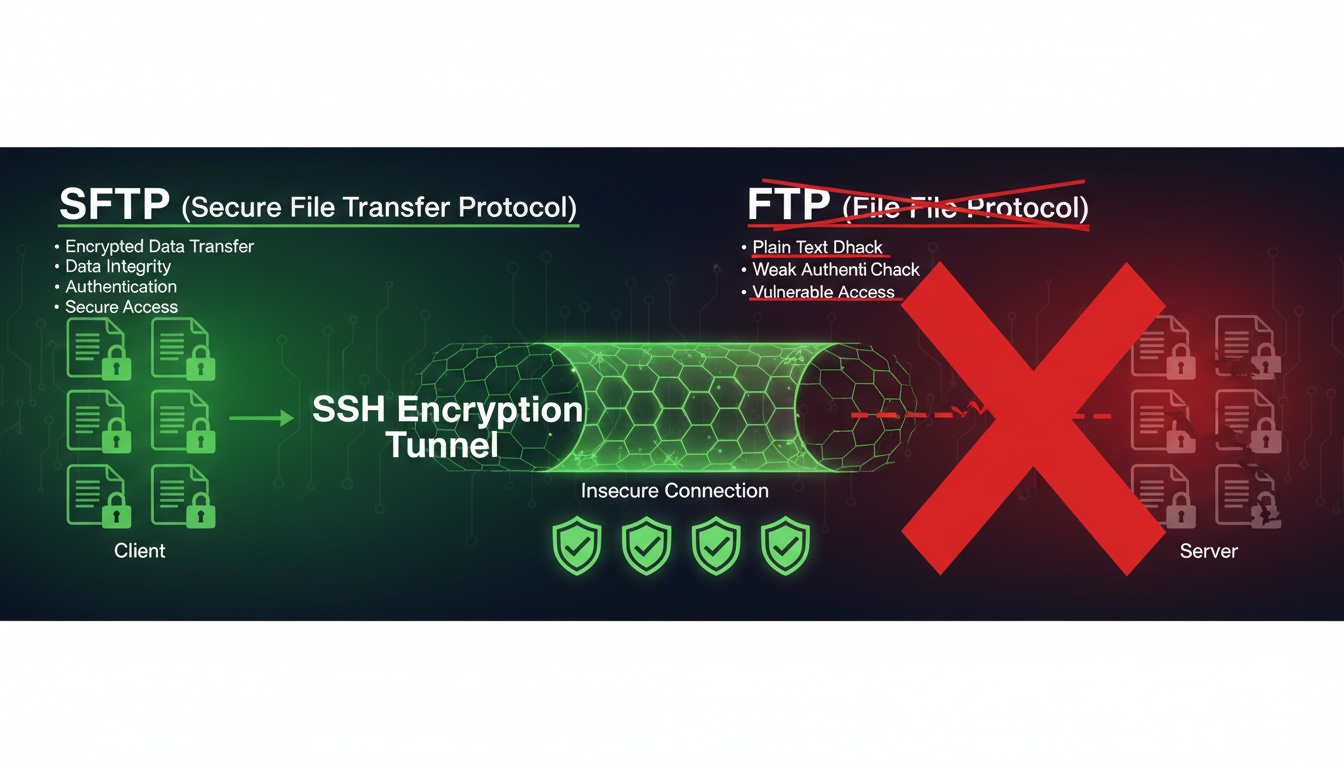
4. Why SFTP Replaced Traditional FTP
Legacy FTP had critical weaknesses:
- Plain text transmission - Credentials and data visible to attackers
- Separate command and data channels - Hard to secure
- Weak authentication - Easily compromised
- No encryption - Data interception risks
SFTP addresses all these issues with robust security mechanisms.
5. Key Advantages of Using SFTP
SFTP provides these significant benefits:
-
End-to-End Encryption
- All data encrypted during transfer
- No plain text exposure
- Protection against man-in-the-middle attacks
-
Strong Authentication
- Public key authentication support
- Multi-factor options
- Certificate-based verification
-
Integrity Protection
- Built-in checksums
- Tamper detection
- Data consistency assurance
-
Comprehensive Logging
- Detailed audit trails
- Compliance reporting
- Security monitoring
-
Single Port Operation
- Uses only port 22
- Simplified firewall configuration
- Reduced attack surface
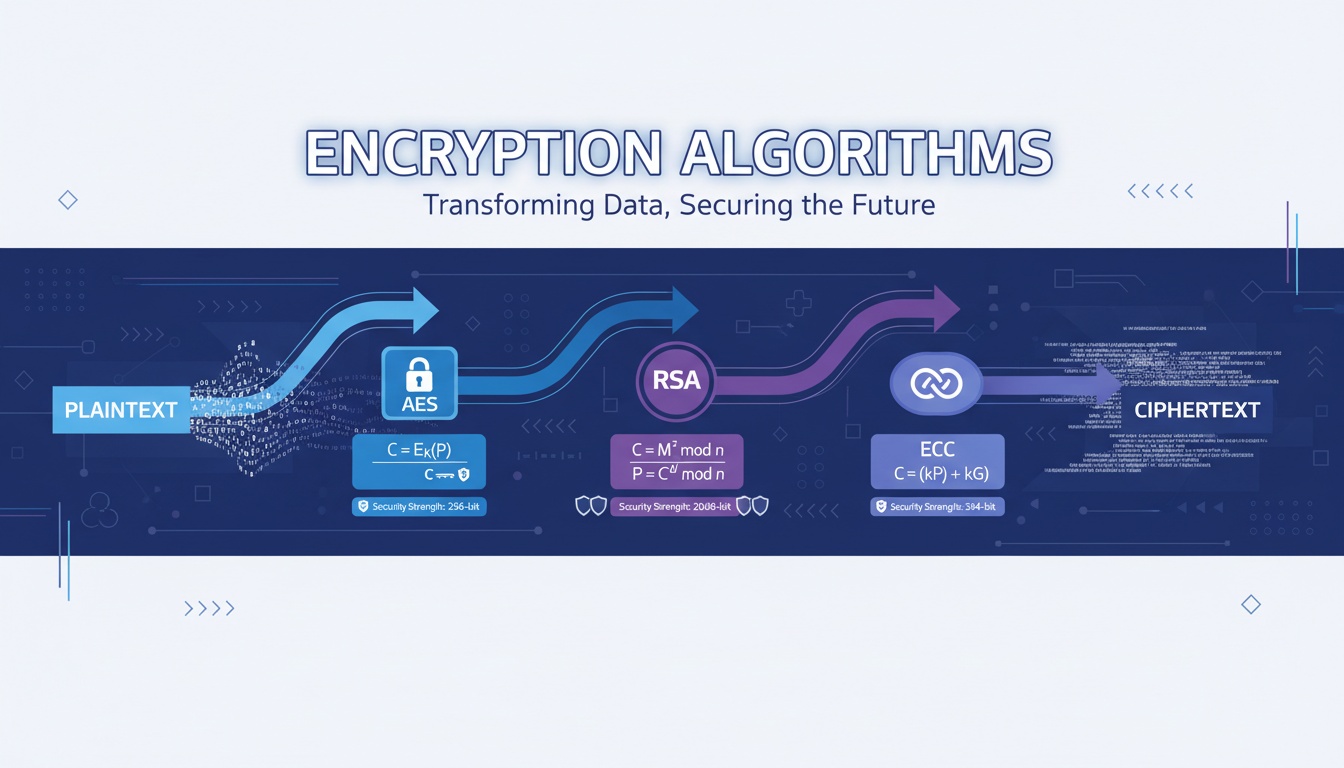
6. How SFTP Encryption Works
SFTP employs multiple encryption layers:
-
Transport Layer Security
- SSH handshake establishes secure channel
- Uses strong cipher suites (AES-256, ChaCha20)
- Perfect forward secrecy support
-
Data Encryption
- Symmetric encryption for file contents
- MAC (Message Authentication Codes) for integrity
- Compression options for performance
-
Key Exchange
- RSA, ECDSA, or Ed25519 algorithms
- Regular key rotation
- Secure key storage
7. Enterprise Use Cases for SFTP
Organizations deploy SFTP for:
Financial Services
- SEC/FINRA compliance
- Customer data transfers
- Interbank communications
Healthcare
- HIPAA-compliant file exchange
- Medical record transfers
- Diagnostic imaging sharing
E-commerce
- Payment data processing
- Inventory synchronization
- Order fulfillment
Government
- Classified document handling
- Citizen service portals
- Inter-agency communications
8. Common SFTP Configuration Options
Administrators typically configure:
- User access controls - Chroot directories, permissions
- Authentication methods - Password, public key, certificate
- Logging levels - Connection, file operations, errors
- Transfer limits - Bandwidth, concurrent sessions
- Security policies - Cipher suites, key sizes
9. Best Practices for SFTP Deployment
Follow these security guidelines:
- Use key-based authentication over passwords
- Implement proper user access controls
- Regularly rotate SSH host keys
- Enable detailed logging and monitoring
- Restrict users to specific directories
- Keep software updated with security patches
- Use strong cipher suites only
- Implement connection rate limiting
10. SFTP vs Alternatives: Protocol Comparison
| Feature | SFTP | FTP | FTPS | SCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Yes (Built-in) | No | Yes (TLS) | Yes |
| Authentication | Strong (Keys/Certs) | Weak (Password) | Moderate | Strong |
| Firewall Friendly | Yes (Single Port) | No (Multiple Ports) | Partial | No |
| Platform Support | Excellent | Universal | Good | Limited |
| Audit Trail | Comprehensive | None | Limited | Minimal |
11. Keyword Integration Zone
secure file transfer protocol • sftp advantages • ssh file transfer • encrypted file transfer • sftp vs ftp • sftp security • file transfer protocol • sftp port
(Each appears once only.)
12. External References
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-ietf-secsh-filexfer
- https://www.ssh.com/academy/ssh/sftp
- https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.04162018.pdf
****
Need help managing secure file transfers, automating workflows, or implementing enterprise-grade SFTP solutions?
Qcecuring delivers secure, compliant file transfer platforms with full audit capabilities.
Final Summary (5 Key Points)
- SFTP encrypts both commands and data unlike traditional FTP
- It operates over a single port (22), simplifying firewall rules
- Key-based authentication provides stronger security than passwords
- Comprehensive logging supports compliance and auditing requirements
- SFTP is the preferred choice for secure enterprise file transfers
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.