Understand what NIST is, why compliance matters, and how SP 800-53 and CSF improve security.
What Is NIST Compliance? (Explained Simply)
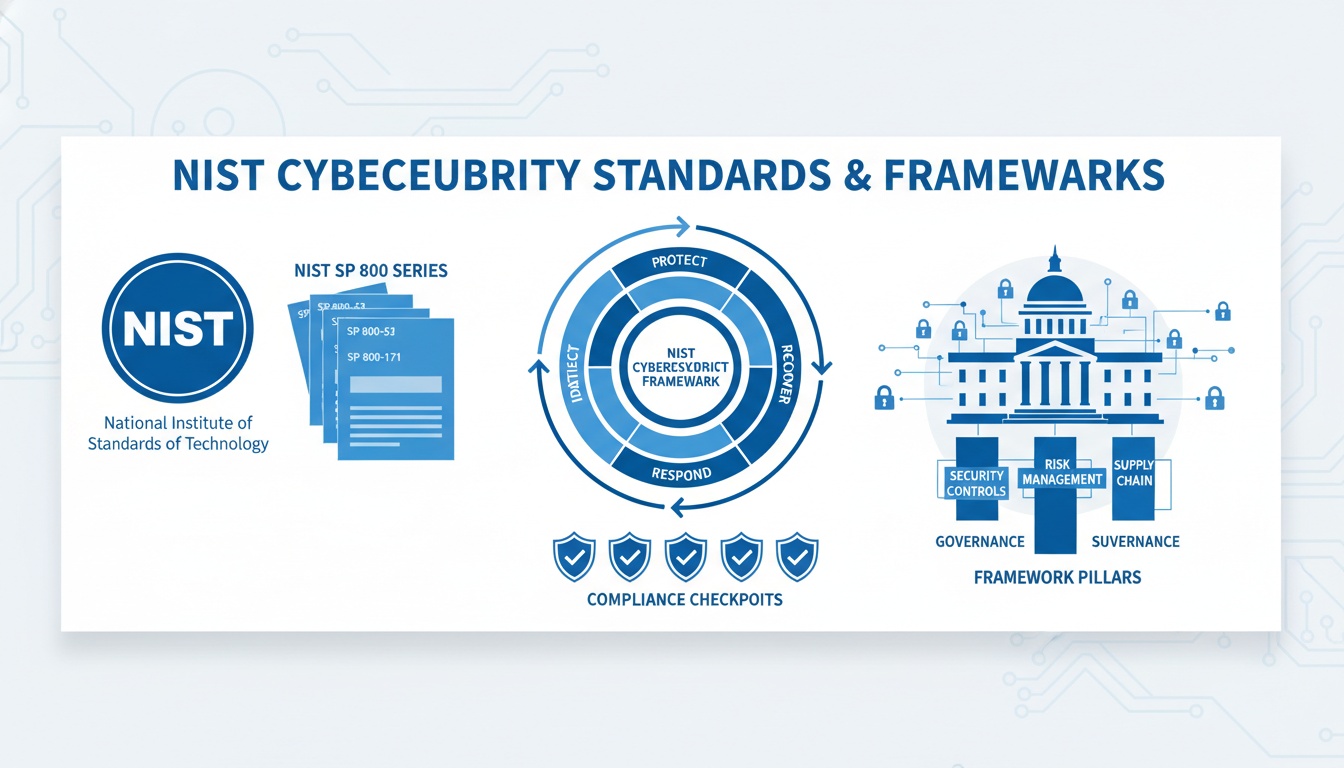
The U.S. government publishes several cybersecurity standards under NIST — the National Institute of Standards and Technology. These standards help organizations protect data, improve security programs, and reduce risk across federal and commercial environments.
NIST compliance means following these standards, implementing the required controls, and maintaining them over time. It gives organizations a clear, measurable approach to cybersecurity and builds trust with customers, stakeholders, and government partners.
This guide explains NIST in a simple, human-friendly way — no jargon, no complexity.
What This Guide Covers
- What NIST is (simple definition)
- Why NIST compliance matters
- Who should comply
- What NIST SP 800-53 includes
- Top 10 NIST security controls
- How NIST compares to ISO, DFARS, and CMMC
- Best practices for 2025
- Keyword coverage without repetition
1. What Is NIST? (Simple Definition)
NIST is a U.S. government organization that creates:
- Technology standards
- Cybersecurity guidelines
- Measurement and testing models
- Security control frameworks
NIST helps organizations protect data, strengthen systems, and maintain consistent security practices. It plays a major role in how businesses, contractors, and government agencies manage cybersecurity.
2. What Does NIST Do?
NIST develops standards that explain how data should be secured, including:
- Minimum security controls
- Risk management best practices
- Guidelines for protecting federal information
- Benchmarks for secure system configuration
Following NIST gives organizations a baseline security foundation that applies across industries — from finance to healthcare to government contracting.
3. What Is NIST Compliance?
NIST compliance means implementing NIST’s security guidelines and maintaining them as threats evolve. It includes:
- Following required security controls
- Protecting sensitive and government data
- Performing assessments and audits
- Updating controls as risks change
Compliance protects organizations, customers, and national security from cyberattacks.
4. Who Needs To Comply With NIST?
NIST compliance applies to:
- U.S. federal agencies
- Government contractors and subcontractors
- Vendors handling federal data
- Organizations preparing to bid on federal projects
- Companies wanting higher cybersecurity trust and maturity
If your business handles federal information — directly or indirectly — you must comply.
5. NIST SP 800-53 (Explained Simply)
NIST SP 800-53 defines the security and privacy controls required to protect federal information systems.
It is one of the most widely used security control catalogs in the world.
Controls are grouped into families such as:
- AC — Access Control
- AU — Audit & Accountability
- CM — Configuration Management
- IR — Incident Response
- MP — Media Protection
- PS — Personnel Security
These controls help organizations secure data, systems, identities, and processes.
6. Top 10 Security Controls in NIST SP 800-53
| Control | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Access Control (AC) | Limits who can access systems and data |
| Audit & Accountability (AU) | Tracks user activity and anomalies |
| Awareness & Training (AT) | Trains staff on security responsibilities |
| Configuration Management (CM) | Secures system configurations |
| Contingency Planning (CP) | Ensures business continuity |
| Identification & Authentication (IA) | Verifies users and devices |
| Incident Response (IR) | Guides response to cyber incidents |
| Maintenance (MA) | Keeps systems updated and secure |
| Media Protection (MP) | Secures physical/digital media |
| Personnel Security (PS) | Reduces insider threats |
These are the building blocks of federal-level cybersecurity.
7. Why NIST Compliance Matters
NIST compliance provides major benefits:
- Protects sensitive and regulated data
- Strengthens overall security posture
- Reduces chances of breaches and downtime
- Enables businesses to qualify for federal contracts
- Builds trust with partners and customers
- Helps organizations meet FISMA, HIPAA, or federal regulations
For many contractors, NIST compliance is a requirement — not an option.
8. NIST vs Other Frameworks (Simple Comparison)
| Standard | Purpose | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| NIST | U.S. federal cybersecurity standards | Free, detailed, widely adopted |
| ISO 27001 | International security standard | Certification-focused |
| DFARS | Defense contractor rules | Procurement-focused |
| CMMC | DoD contractor certification | Mandatory for defense vendors |
NIST is the most detailed and often the foundation for other frameworks.
9. Best Practices for NIST Compliance (2025)
- Apply least privilege access across all systems
- Enable MFA for every identity
- Maintain a complete asset inventory
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit
- Centralize logging and monitoring
- Conduct regular audits and gap assessments
- Train employees on security behavior
- Document policies and evidence clearly
- Monitor third-party and supply chain risks
- Automate compliance checks where possible
10. External References
- https://www.nist.gov
- https://www.cisa.gov
- https://cloudflare.com/learning
- https://learn.microsoft.com/security
- https://www.rfc-editor.org
****
Need help implementing NIST controls, automating compliance, or modernizing your certificate and identity security program?
Qcecuring delivers automated, cloud-ready PKI and cybersecurity solutions.
Final Summary (5 Key Points)
- NIST compliance strengthens cybersecurity across all industries.
- SP 800-53 provides detailed controls for protecting systems and data.
- Compliance is essential for government agencies and contractors.
- Following NIST reduces risk, supports audits, and improves trust.
- Organizations of any size can adopt NIST to boost security maturity.
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.