A simple, human-friendly explanation of BYOE, HYOK, cloud encryption control, and HSM-backed key ownership.
What Is BYOE? (Explained Simply)
As more organizations move their data to the cloud, one concern keeps coming up:
“Who controls the encryption keys that protect our data?”
Cloud providers usually offer encryption, but some organizations hesitate to rely entirely on them. They want stronger control, independence, and the ability to choose how their keys are generated, stored, and used.
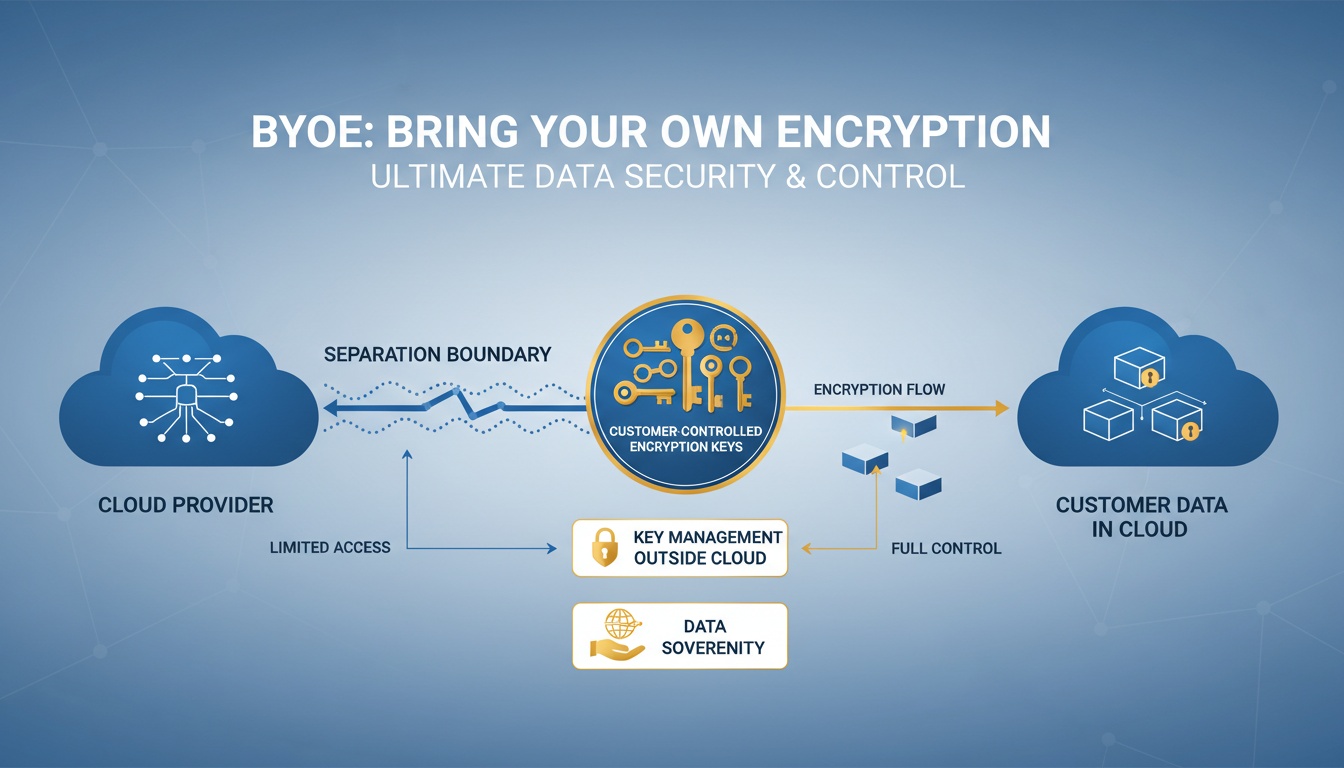
This is where BYOE — Bring Your Own Encryption — comes in. Also called HYOK (Hold Your Own Key), BYOE gives organizations complete control of their encryption keys, even when their data lives in the cloud.
What This Guide Covers
- What BYOE (HYOK) means
- Why organizations use their own encryption
- Benefits of BYOE
- How HSMs support BYOE
- Difference between BYOE and BYOK
- Best practices for using BYOE
- Keyword integration without repetition
1. What Is BYOE? (Simple Definition)
BYOE (Bring Your Own Encryption) is a security model where the organization — not the cloud provider — fully controls the encryption keys used to protect cloud data.
Key points:
- You own the keys
- You manage the keys
- You control the cryptographic operations
- The cloud provider never sees or stores your keys
In BYOE, an HSM (Hardware Security Module) typically acts as a secure proxy. It performs all encryption and decryption operations without exposing keys to the cloud environment.
2. BYOE vs BYOK (Clear Difference)
Many people confuse BYOE with BYOK.
-
BYOK (Bring Your Own Key)
You import your key into the cloud provider’s system. -
BYOE (Bring Your Own Encryption / HYOK)
You never give the cloud provider a copy of your key.
All cryptography happens in your own HSM.
If an organization wants maximum independence and control, BYOE is the stronger model.
3. Why Organizations Choose BYOE
BYOE is becoming more popular in regulated industries, global enterprises, and security-conscious teams. Here’s why:
1. Enhanced Data Control
Your keys stay with you, not with the cloud provider. Even during a breach, the provider cannot decrypt your data.
2. Compliance Requirements
Some standards require complete key control:
- Financial regulations
- Government and defense requirements
- Healthcare data protection mandates
3. No Vendor Lock-in
Switching cloud providers becomes painless if your encryption keys and processes never depend on the provider’s system.
4. Improved Transparency
You can independently verify your encryption posture instead of relying solely on cloud audit reports.
5. Better Disaster Recovery
If a cloud outage occurs, you retain key access and can decrypt data when moving or restoring workloads.
6. Freedom to Choose Encryption Algorithms
You can use algorithms that meet your regulatory, performance, or regional requirements.
7. Future-Proof Security
When new cryptographic standards emerge (e.g., post-quantum), you can adopt them without waiting for a cloud provider.
4. Benefits of BYOE (Summary Table)
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Key Ownership | You fully control encryption keys |
| Compliance Support | Helps satisfy strict data protection laws |
| Avoid Vendor Lock-In | Easily migrate between cloud providers |
| Increased Trust | Independent assurance over encryption |
| Stronger DR | Keys remain accessible even during cloud outages |
| Algorithm Choice | Select your preferred encryption mechanisms |
5. How HSMs Support BYOE
An HSM (Hardware Security Module) is a tamper-resistant device that protects cryptographic keys and performs encryption in a secure environment.
In BYOE, HSMs:
1. Store and Protect Keys
Your keys never leave the HSM or appear inside the cloud provider’s systems.
2. Perform Encryption & Decryption
The HSM handles:
- Key generation
- Data encryption
- Data decryption
- Signing operations
3. Act as a Secure Proxy
The HSM sits between your infrastructure and the cloud, ensuring cryptography happens in a trusted environment.
This design gives you complete ownership of your cryptographic lifecycle.
6. Why BYOE Matters in 2025
Cloud adoption is accelerating, and so are regulatory requirements. BYOE helps organizations:
- Strengthen cloud security
- Maintain sovereignty over sensitive data
- Reduce reliance on any single provider
- Meet global privacy expectations
- Protect workloads across hybrid and multi-cloud environments
For industries like finance, healthcare, energy, and government, BYOE is fast becoming the preferred model for cloud encryption.
7. Best Practices for BYOE (2025)
- Use certified HSMs (FIPS 140-2 or 140-3)
- Keep keys entirely outside cloud infrastructure
- Implement strict access controls for key usage
- Enable detailed logging for all cryptographic operations
- Use strong algorithms (AES-256, RSA-2048/ECDSA)
- Map BYOE processes to compliance frameworks
- Automate key rotation and revocation
- Regularly audit your HSM access policies
8. External References
- https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/cryptographic-key-management — NIST guidance on key management used in BYOE/HYOK models
- https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/blog/2021/12/13/byok-byog-byoh-byokm/ — CSA explanation of BYOK, BYOE, HYOK, and cloud encryption ownership
- https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/fundamentals/hold-your-own-key — Microsoft “Hold Your Own Key (HYOK)” documentation
- https://cloud.google.com/security/encryption/default-encryption — Google Cloud encryption architecture and customer-controlled key concepts
- https://aws.amazon.com/kms/features/#Bring_Your_Own_Key — AWS BYOK/BYOE concepts via customer-controlled keys
****
Need help deploying BYOE, managing HSMs, or designing secure multi-cloud encryption architectures?
Qcecuring builds modern encryption, PKI, and key-management solutions for enterprises.
Final Summary (5 Key Points)
- BYOE keeps your encryption keys fully under your control.
- It prevents vendor lock-in and strengthens data sovereignty.
- HSMs enable secure key storage and cryptographic operations.
- BYOE supports strict compliance and privacy requirements.
- It is ideal for cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.