A beginner-friendly yet in-depth guide to SHA-256 hashing, how the algorithm works, its use cases, advantages, hash length, security level, and why SHA-256 remains the trusted standard in 2025.
SHA-256
Cryptography keeps our digital world secure — from your banking apps to blockchain networks to SSL certificates.
And at the center of many of these systems sits one powerful algorithm:
SHA-256 — the 256-bit Secure Hash Algorithm used almost everywhere security matters.
This guide explains SHA-256 in a simple and human tone — without losing technical accuracy.
1. What Is SHA-256?
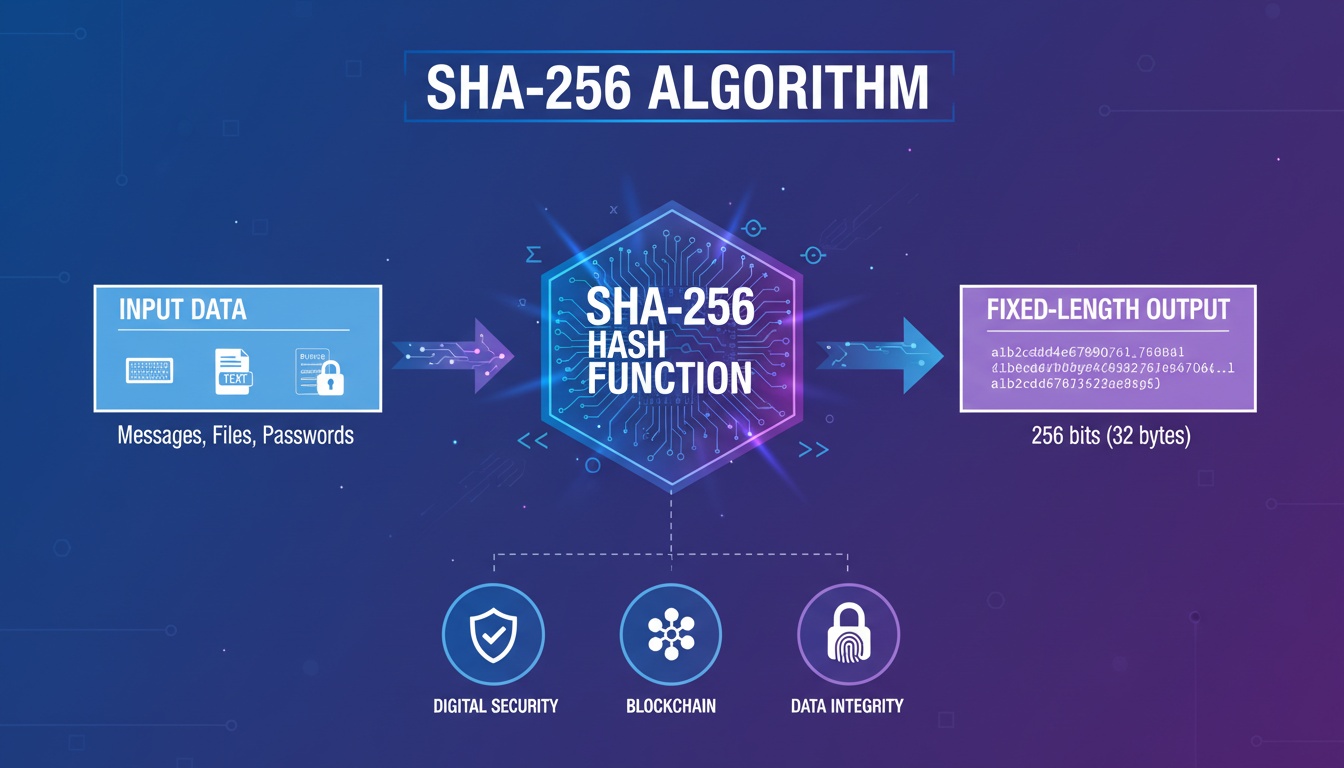
SHA-256 is a cryptographic hash function from the SHA-2 family, designed by NIST and NSA.
Its job is to convert any data into a fixed 256-bit hash value.
A SHA-256 hash:
- is always 64 hexadecimal characters
- is always 256 bits long
- changes completely if the input changes even slightly
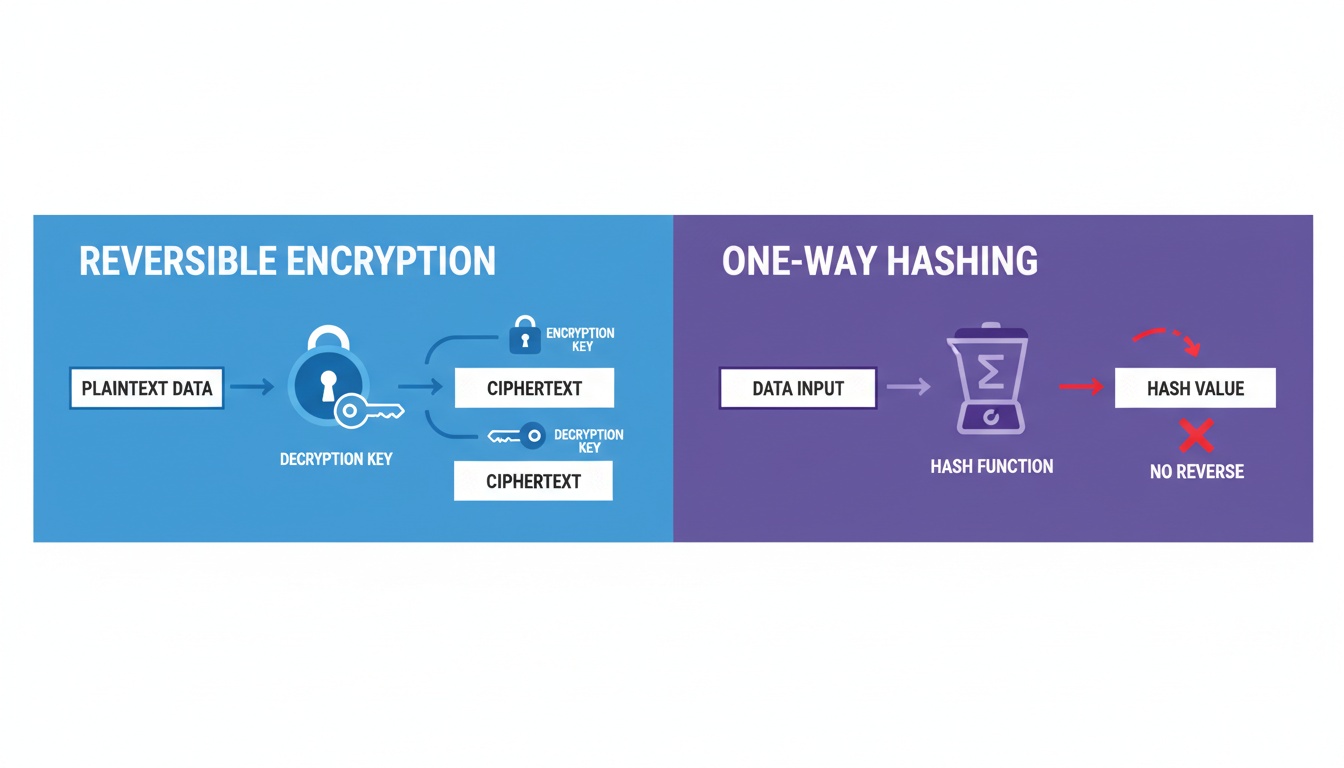
- cannot be reversed
SHA-256 is NOT encryption
A very common misconception.
- Encryption = reversible
- Hashing = permanent, one-way
So terms like “sha256 decryption” or “sha256 decode” are technically incorrect.
Example SHA-256 output:
0109fca76b36f908442a66d57fc507618997ff4aebc2c083d7795ca3be3f5d1a
2. How Does SHA-256 Work?
Let’s hash the message:
“Hello, SHA-256!”
Here’s what SHA-256 does internally:
Step 1 — Convert the message to binary
Every character becomes an ASCII-based binary sequence.
Step 2 — Message Padding
SHA-256 processes data in 512-bit blocks, so it:
- appends a
1bit - adds necessary
0bits - appends the original message length
Step 3 — Initialize Internal Hash Values
SHA-256 uses 8 fixed 32-bit constants as the starting state.
Step 4 — Process the Message in Blocks
Each block goes through:
- XOR
- right rotations
- modular additions
- message scheduling
- 64 compression rounds
This is the core of the algorithm.
Step 5 — Produce the Final 256-Bit Hash
After processing all blocks, you get your final 256-bit (64-character) digest.
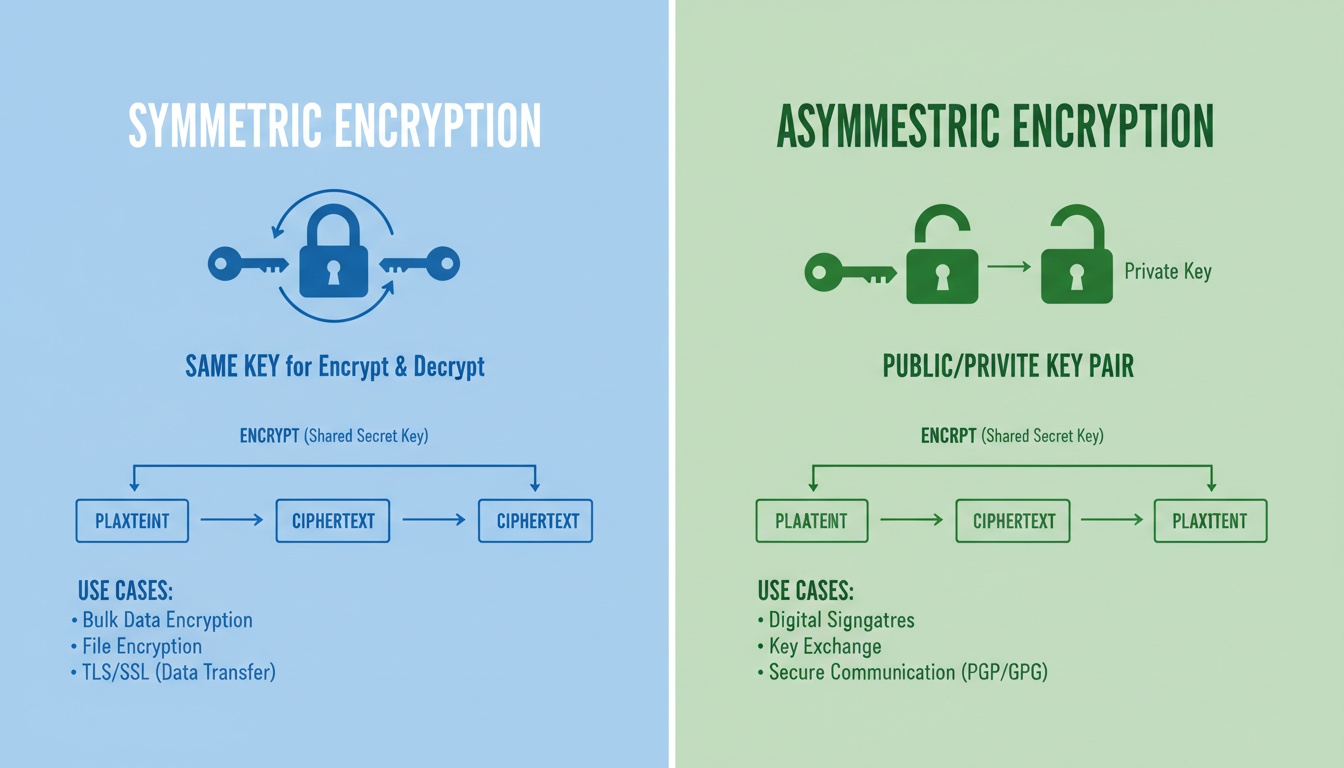
3. Why SHA-256 Is Important (Advantages)
Strong Data Integrity
Any tiny change in input gives a completely different hash.
Collision Resistant
Two different inputs shouldn’t produce the same hash.
Industry Standard
Used in:
- Blockchain
- TLS/SSL Certificates
- Digital Signatures
- File integrity systems
Fast and Efficient
Highly optimized for modern hardware.
Trusted Successor to SHA-1
SHA-1 is broken; SHA-256 is secure.
4. Limitations of SHA-256
Not reversible (cannot decrypt)
Hashes cannot be turned back into original data.
Deterministic
Same input → same hash
This can expose weak passwords if not salted.
Not suitable for password storage alone
Use:
- Argon2
- bcrypt
- PBKDF2
- scrypt
Theoretical collision possibility
Although never found in practice.
5. Where Is SHA-256 Used?
SHA-256 is everywhere modern security exists.
1. Digital Signatures (RSA SHA-256 / ECDSA)
Used to verify:
- documents
- software
- certificates
- code signing
2. Blockchain Technology (Bitcoin, etc.)
Bitcoin uses:
- SHA-256 for block hashing
- SHA-256 mining
- double SHA-256 for block generation
3. SSL/TLS Certificates (CAs)
Certificate Authorities sign certificates using:
- RSA-SHA256
- ECDSA-SHA256
This ensures authenticity and integrity.
4. File Integrity Checking
Tools like:
sha256sum- checksum verifiers
- installers
help confirm files haven’t been tampered with.
5. Secure Communications (TLS, SSH, IPsec)
Used to validate data integrity during transmission.
6. SHA-256 Hash Length & Size
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Hash length (hex) | 64 characters |
| Hash length (bits) | 256 bits |
| Hash length (bytes) | 32 bytes |
| Block size | 512 bits |
7. SHA-2 vs SHA-256 vs SHA-512 (Short Comparison)
| Algorithm | Output | Speed | Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| SHA-1 | 160 bits | Fast | Broken |
| SHA-256 | 256 bits | Good | Secure |
| SHA-512 | 512 bits | Faster on 64-bit CPUs | Very Secure |
| SHA-2 Family | 224/256/384/512 | Varies | Trusted Standard |
8. Is SHA-256 Still Secure in 2025?
Yes — SHA-256 is still extremely secure.
There are:
- no practical collisions
- no real-world breaking attacks
- billions of devices that rely on it daily
It remains a top choice for hashing in security-critical systems.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
Is SHA-256 encryption?
No — it’s a one-way hashing function.
Can SHA-256 be decrypted?
No. It is mathematically irreversible.
How does SHA-256 work?
Through padding, block processing, and 64 compression rounds.
Is SHA-256 safe?
Yes — SHA-256 is safe and widely trusted.
SHA-1 vs SHA-256?
SHA-256 is far more secure.
10. Summary
- SHA-256 is a secure, 256-bit hashing algorithm.
- It can’t be reversed or decrypted.
- It powers blockchain, digital signatures, certificates, and integrity systems.
- It remains secure and trusted in 2025.
11. Need Help With Hashing, Certificates or PKI Automation?
If you want expert help with:
- SHA-256 implementation
- enterprise PKI
- certificate lifecycle automation
- secure hashing strategy
- cryptographic design
Our team can guide you.
Book a Demo: https://qcecuring.com/request-demo
Talk to our Security Experts
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.