A simple, modern deep-dive into cryptography, its types, and real-world applications
Opening Section
Cryptography is the foundation of modern digital security. Every secure message, encrypted file, protected login session, and private online transaction depends on cryptographic techniques. From symmetric algorithms to modern public key systems, cryptography ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation across global networks.
This guide provides a clear, modern, and fully original explanation of what cryptography is, why it matters in cybersecurity, and how real cryptographic systems work in practice across cloud environments, enterprise applications, and modern identity workflows.
What This Guide Covers
- Simple definition of cryptography
- Core goals of cryptographic systems
- Types of cryptography (symmetric, asymmetric, hashing)
- How cryptographic algorithms work internally
- Step-by-step encryption workflow
- Common attacks and how to avoid them
- Real code examples
- Best practices for secure implementation
- Cloud-native and enterprise use cases
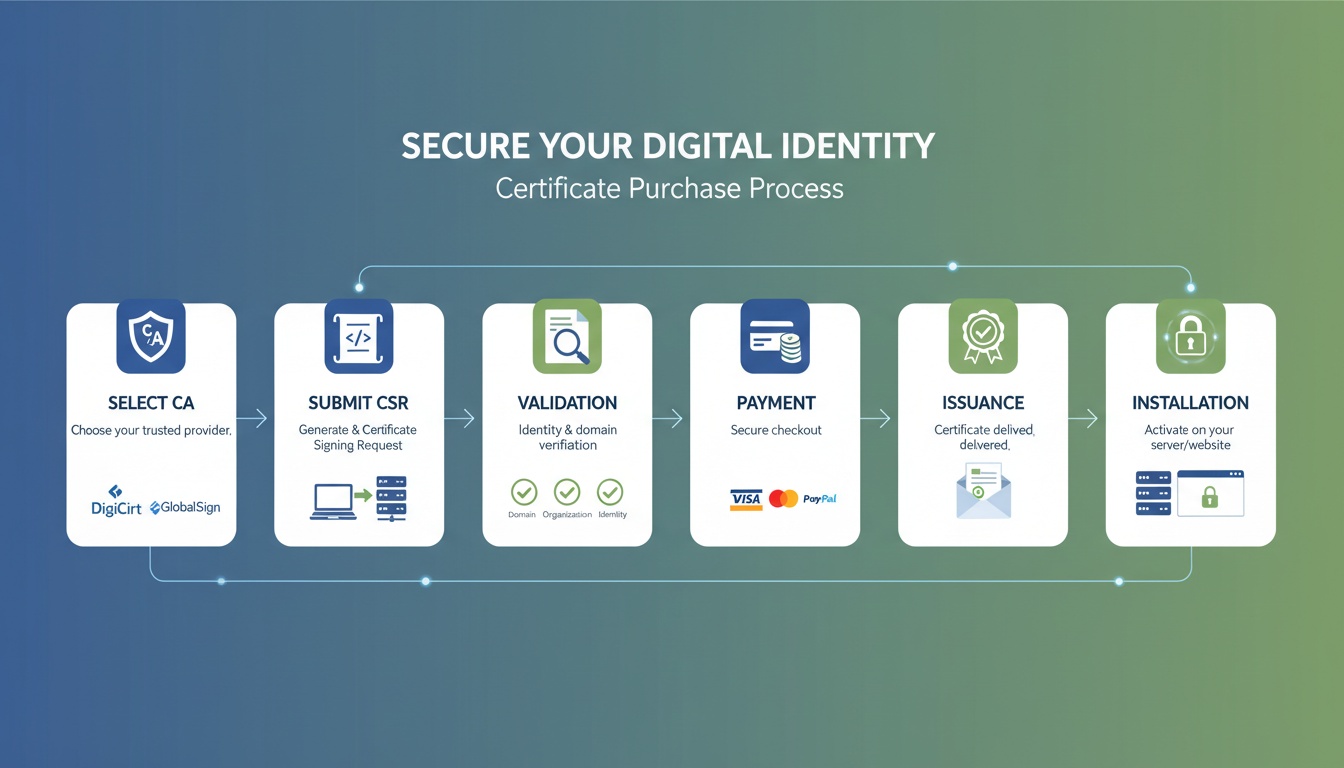
Workflow Diagram (AI-Generated)
Alt-text: High-level workflow of cryptography processes
1. What Is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the science of securing information through mathematical techniques. It transforms readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable form (ciphertext) and ensures that only authorized parties can access or modify it.
Cryptography provides four essential security properties:
- Confidentiality — Protecting data from unauthorized access
- Integrity — Ensuring data is not altered
- Authentication — Verifying identities
- Non-repudiation — Preventing denial of actions
Cryptography is used in:
- Network security
- Cloud applications
- Secure messaging
- Payment systems
- VPNs and Wi-Fi security
- Identity and access management
- IoT device communication
2. Why Cryptography Matters Today
Modern organizations depend heavily on cryptography, especially as systems move to the cloud, mobile, and distributed environments.
Key reasons cryptography is essential:
- Protects sensitive data from breaches
- Secures communication over untrusted networks
- Enables identity verification (certificates, MFA, SSO)
- Required for compliance (NIST, PCI-DSS, ISO, HIPAA)
- Enables secure cloud workloads and zero-trust architectures
- Used in every major security protocol (TLS, SSH, IPSec)
- Powers encryption for both data-at-rest and data-in-transit
Authoritative References
- https://www.nist.gov
- https://www.cisa.gov
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cryptography
- https://learn.microsoft.com/security
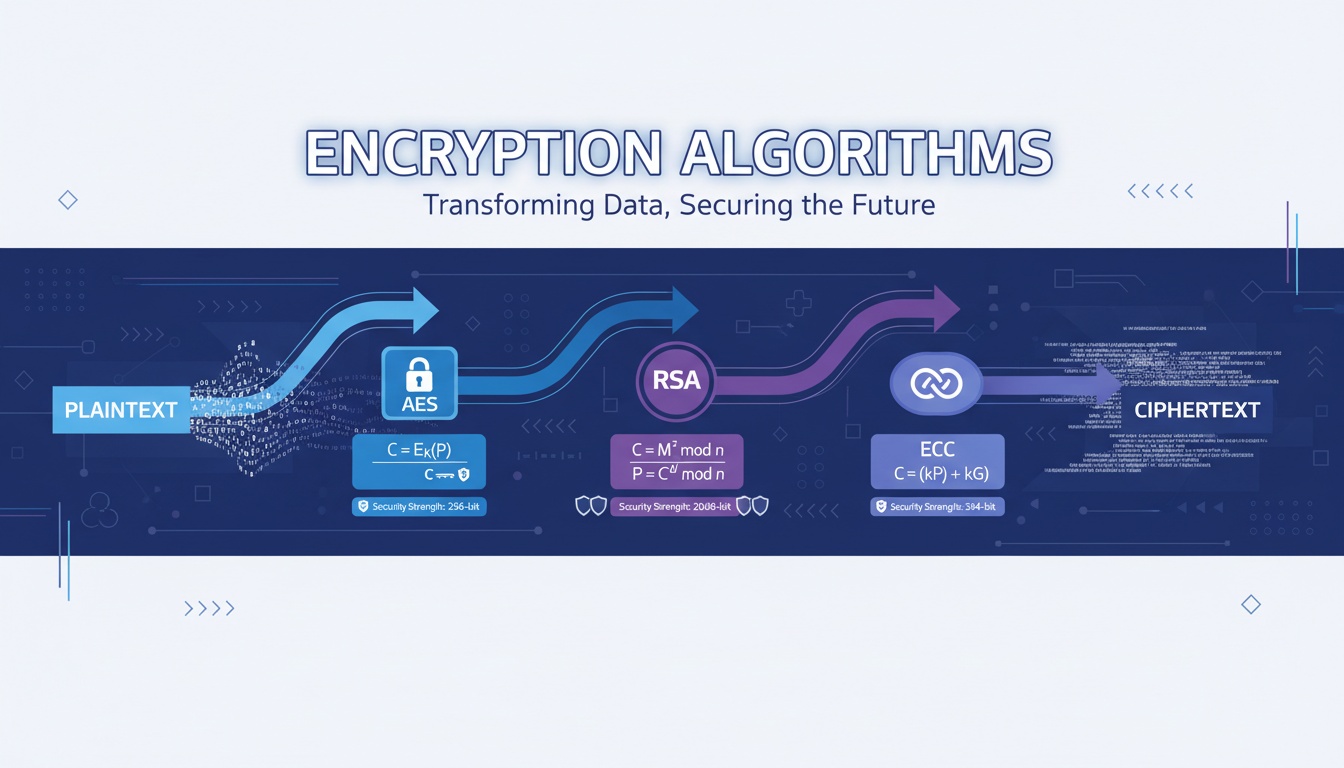
3. How Cryptography Works (Technical Deep Dive)
Cryptography relies on mathematical algorithms and keys to protect information. There are three major categories:
** Symmetric Cryptography**
Same key is used for encryption and decryption.
Examples:
- AES
- ChaCha20
Strengths:
- Fast
- Ideal for bulk data encryption
Weakness:
- Key distribution is challenging
** Asymmetric Cryptography (Public Key Cryptography)**
Uses a keypair: public key + private key.
Examples:
- RSA
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Strengths:
- Secure key exchange
- Digital signatures
Weakness:
- Slower than symmetric crypto
** Cryptographic Hashing**
One-way mathematical transformation.
Examples:
- SHA-256
- SHA-3
Used for:
- Password hashing
- Integrity checks
- Blockchain
4. Architecture Workflow (Step-by-Step)
- User or application generates plaintext
- A key (symmetric or asymmetric) is selected
- Encryption algorithm transforms plaintext → ciphertext
- Ciphertext is transmitted or stored
- Receiver verifies integrity (optional hashing/MAC)
- Receiver decrypts using appropriate key
- Plaintext is recovered securely
This workflow is the basis for secure messaging, TLS handshakes, file encryption, and API security.
5. Real Code Snippets (Python + OpenSSL)
Hashing with SHA-256 (Python)
import hashlib
data = b"hello world"
digest = hashlib.sha256(data).hexdigest()
print("SHA256:", digest)Symmetric Encryption (Fernet / AES wrapper)
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
key = Fernet.generate_key()
cipher = Fernet(key)
token = cipher.encrypt(b"example message")
print("Encrypted:", token)
print("Decrypted:", cipher.decrypt(token))Generate RSA Keypair (OpenSSL)
openssl genrsa -out private.key 2048
openssl rsa -in private.key -pubout -out public.key6. Best Practices (Must Follow)
- Use strong algorithms (AES-256, RSA-2048+, ECC-P256)
- Avoid outdated algorithms (DES, MD5, SHA-1)
- Use authenticated encryption (AES-GCM, ChaCha20-Poly1305)
- Always validate certificates and signatures
- Protect private keys in hardware (HSM, TPM, KMS)
- Rotate keys periodically
- Enforce HTTPS/TLS 1.3 everywhere
- Avoid building your own cryptography
- Use secure randomness for key generation
- Hash passwords with bcrypt/Argon2
- Perform integrity checks on all sensitive data
7. Common Pitfalls
- Reusing encryption keys
- Using hardcoded keys in code
- Weak key generation methods
- Incorrect IV/nonce handling
- Storing private keys in plain text
- Using broken algorithms like DES
- No certificate validation in applications
- Misconfigured TLS settings
- Skipping hashing for integrity
- Not rotating keys regularly
8. Advanced Use Cases
- Zero-trust architecture security
- Secure Kubernetes communication (mTLS)
- IoT device authentication
- Encrypted database storage
- Cloud KMS integrations (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Certificate-based authentication for APIs
- Blockchain transaction verification
- Secure boot and firmware validation
9. Keyword Expansion Zone
- cryptography types and methods
- how does cryptography work step by step
- symmetric vs asymmetric cryptography
- cryptography in cyber security
- cryptographic security concepts
- cryptography techniques explained
Comparison Table
| Feature | Symmetric Crypto | Asymmetric Crypto |
|---|---|---|
| Keys Used | One shared key | Public + private key |
| Speed | Very fast | Slower |
| Use Case | Bulk encryption | Key exchange, signatures |
| Algorithms | AES, ChaCha20 | RSA, ECC |
| Security | High | High (larger key sizes needed) |
External Resources
- https://www.nist.gov
- https://cisa.gov
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning
- https://learn.microsoft.com/security
- https://www.rfc-editor.org
Looking to implement secure, scalable certificate lifecycle automation across your enterprise?
Qcecuring helps you modernize PKI, SSH, SSL, and code signing workflows with cloud-native automation.Book a Demo: https://qcecuring.com/request-demo
Final Summary
- Cryptography secures modern digital communication.
- It includes symmetric, asymmetric, and hashing techniques.
- Strong cryptography protects confidentiality, integrity, and authentication.
- Real-world systems rely on cryptography for secure cloud, identity, and network operations.
- Proper key management and modern algorithms are essential for strong security.
Ready to Secure Your Enterprise?
Discover how QCecuring can help you automate certificate lifecycle management, secure SSH keys, and protect your cryptographic infrastructure.